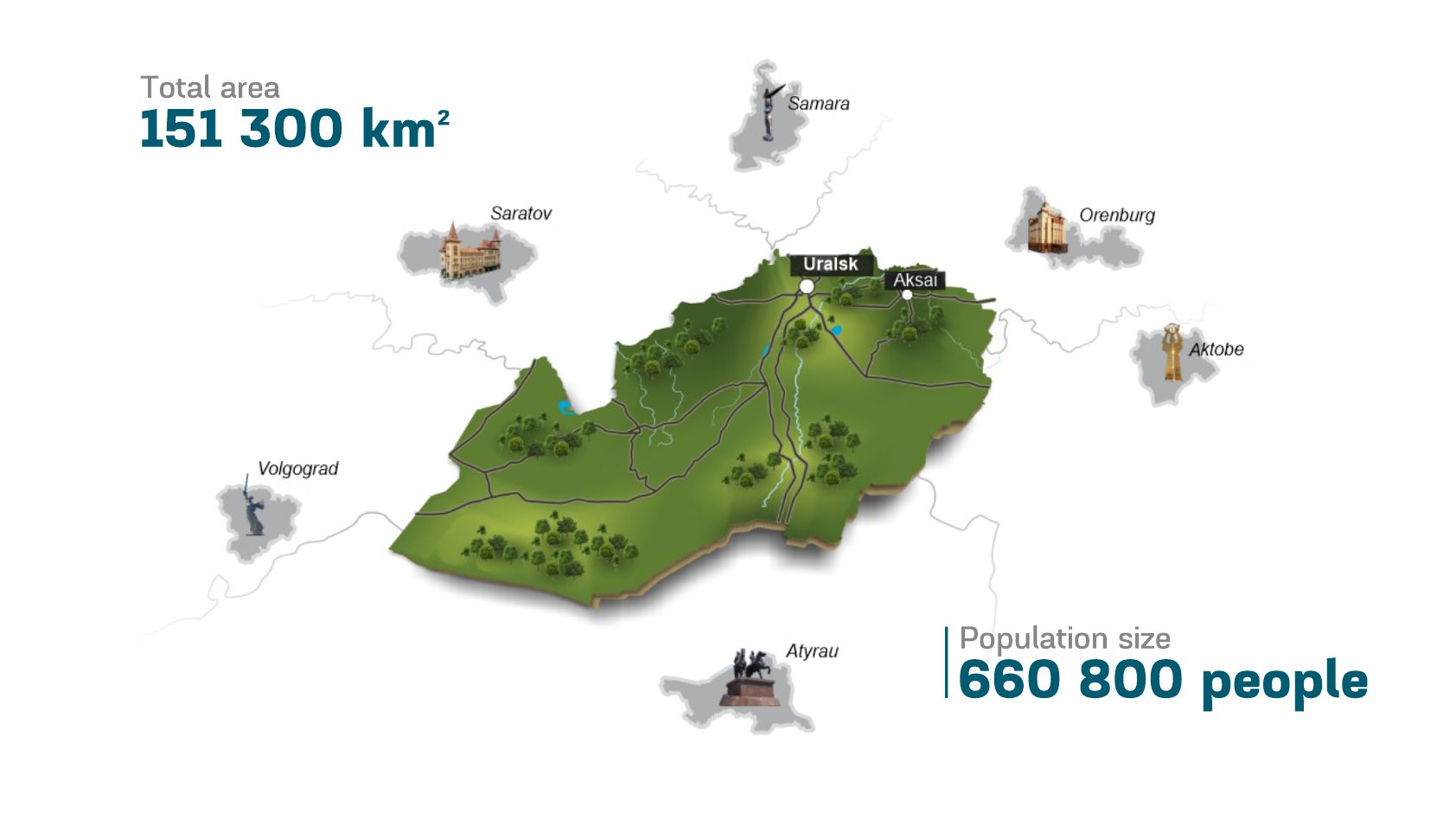
West Kazakhstan region is located in the northwestern part of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The territory of the region is 151.3 thousand square km or 5.6% of the territory of the republic. West Kazakhstan region stretches from north to south for 425 km and from west to east for 585 km.
The region was formed on March 10, 1932. The regional center is Uralsk. The administrative-territorial division of the region includes 2 cities (the city of Uralsk of regional status, the city of Aksai of district status), 12 administrative districts, 3 settlements, and 443 rural settlements.
West Kazakhstan region belongs to the Western macro-region, specializing in the oil and gas industry, engineering, food industry, construction industry, grain farming and animal husbandry.
In the region, the population density is 4.2 people per square km, which is higher compared to Aktobe (2.8 people per sq. km) and Mangistau (3.9 people per sq. km) areas.
Natural and climatic conditions
The relief of the territory of the region is a component of Eastern Europe; it is mainly a flat territory, falling from the northeast to the south-west, divided into five geomorphological regions.
On the territory of the West Kazakhstan region from north to south in the soil cover, the following soil types are distinguished: southern humus, dark chestnut, chestnut and brown soil. Mostly grassland, grass and wormwood, wormwood vegetation.
The climate of the region has a number of features. It is sharply continental with cold winters and hot dry summers, late autumn and early spring frosts, winter thaws and insufficient unstable atmospheric moisture.
January isotherms –11*C, July + 24*С, annual precipitation falls on average 300 mm. Droughts often occur.
In the area there are dangerous meteorological phenomena: drought, dust and sand storms, hail, blizzards with frost, ice.
The rivers of the West Kazakhstan region comprise about 200 rivers and streams, the total length of which, not counting the Ural River, is 4,600 km. The main river of the region, crossing it from north to south, is the Ural River. This river originates in the Ural Mountains at an altitude of more than 600 m. The total length of the Ural River is 2354 km, and within the territory of the region - 500 km. Ural flows through the Caspian lowlands and flows into the Caspian Sea. The supply of rivers is mixed: snow, groundwater and precipitation.
On the territory of the region there are 3260 lakes, the total area is 960 sq. km. Nevertheless, of such a large number of only 84 lakes have an area of more than 1 sq. km. In the summer season, the water surface of the lakes decreases sharply, and small lakes are completely dry by the end of summer. Most flood-type lakes are in the valley of the Ural River. These are usually old lakes, formed in the old meanders of the riverbed.
The largest lake is Lake Chelkar, which is located 70 km to the south-east of the city of Uralsk. The area of this lake, even in very dry years, exceeds 191 sq. km. This is due to the fact that a feed channel was constructed from the Ural River to the lake. The Solyanka River flows out of Chelkar - a tributary of the Ural River, which during the high floods of the Ural River changes its direction and does not flow from the lake, but on the contrary - from the Ural River to the lake.
West Kazakhstan region is located in the steppe and semi-desert natural zone.
By the nature of natural resources and predominantly developed industries, the region can be divided into two parts:
- North: there are enterprises of the oil and gas industry, engineering and metalworking, light and food industries, developed industry of building materials and industry, grain production, developed dairy and cattle breeding, pig breeding and poultry farming;
- South: repair of agricultural machinery, the production of local building materials, developed beef cattle, pasture-meat and meat and sheep breeding, herd horse breeding.
Infrastructure

Economic
Facts and figures:
- 0.1% - growth of the economy of the West Kazakhstan region for 9 months in 2020 (GRP)
- 49.7% of the GRP is produced by an industrial complex; including 4.7% is accounted for processing.
- 3.7% - growth in industrial output in 2020.
- 4.8% - growth in the mining industry in 2020.
- GRP per capita for 9 months of 2020 amounted to 2915.8 thousand tenge, which is 19.2% higher than the national average.
- In 2020, agricultural products were produced in the amount of 200,4 billion tenge.
- By the end of 2020, investments were raised in the amount of 467,5 billion tenge.
